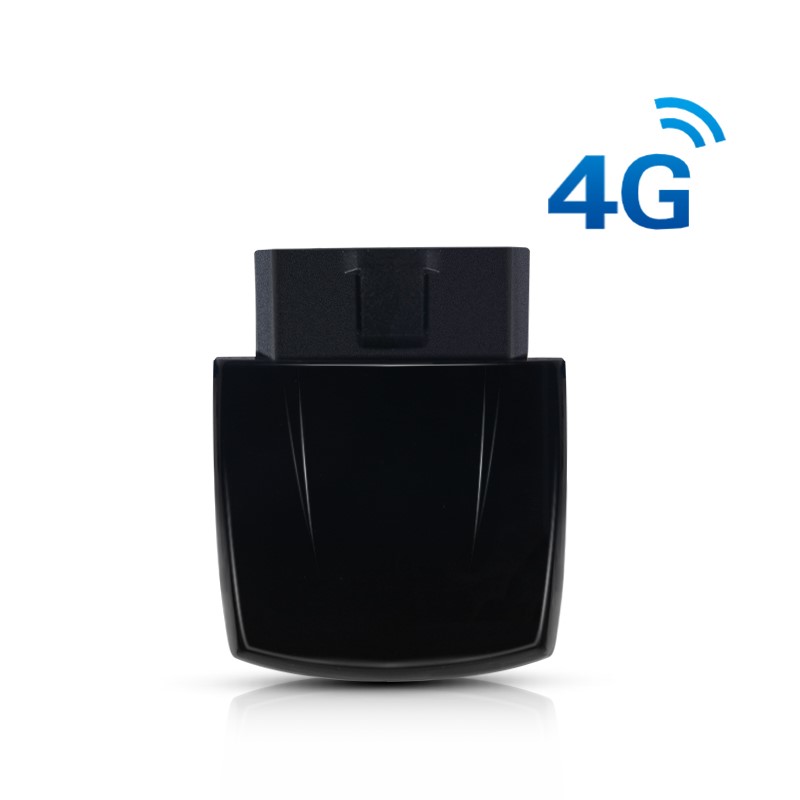
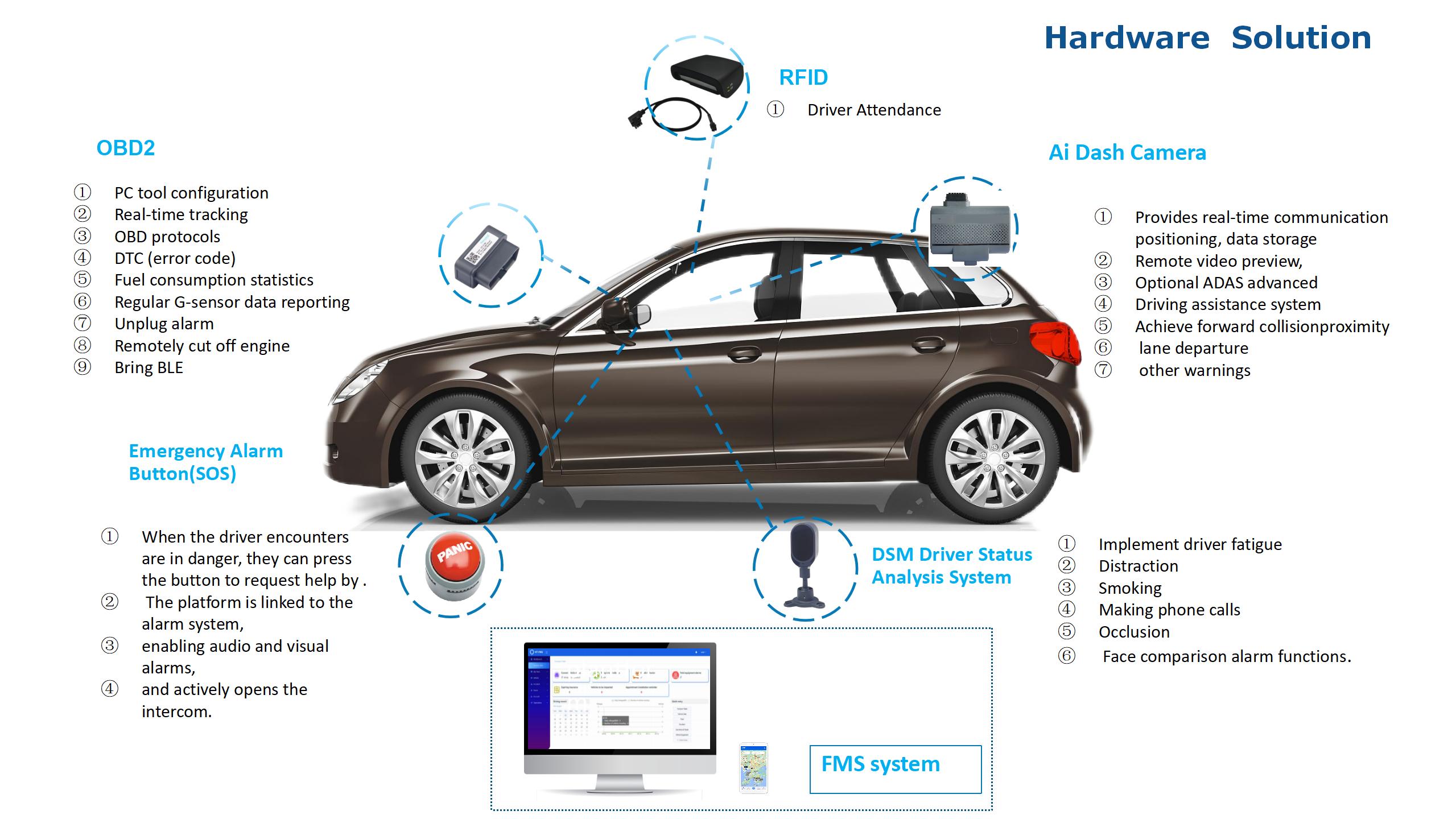
The integration of OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) technology with fleet management systems has revolutionized the way businesses monitor and manage their vehicles. OBD2, a standardized system in most vehicles manufactured after 1996, provides real-time data about a vehicle’s performance, including engine status, fuel efficiency, emissions, and diagnostic trouble codes. This data is invaluable for fleet management systems, which rely on accurate and timely information to optimize operations, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with regulations.

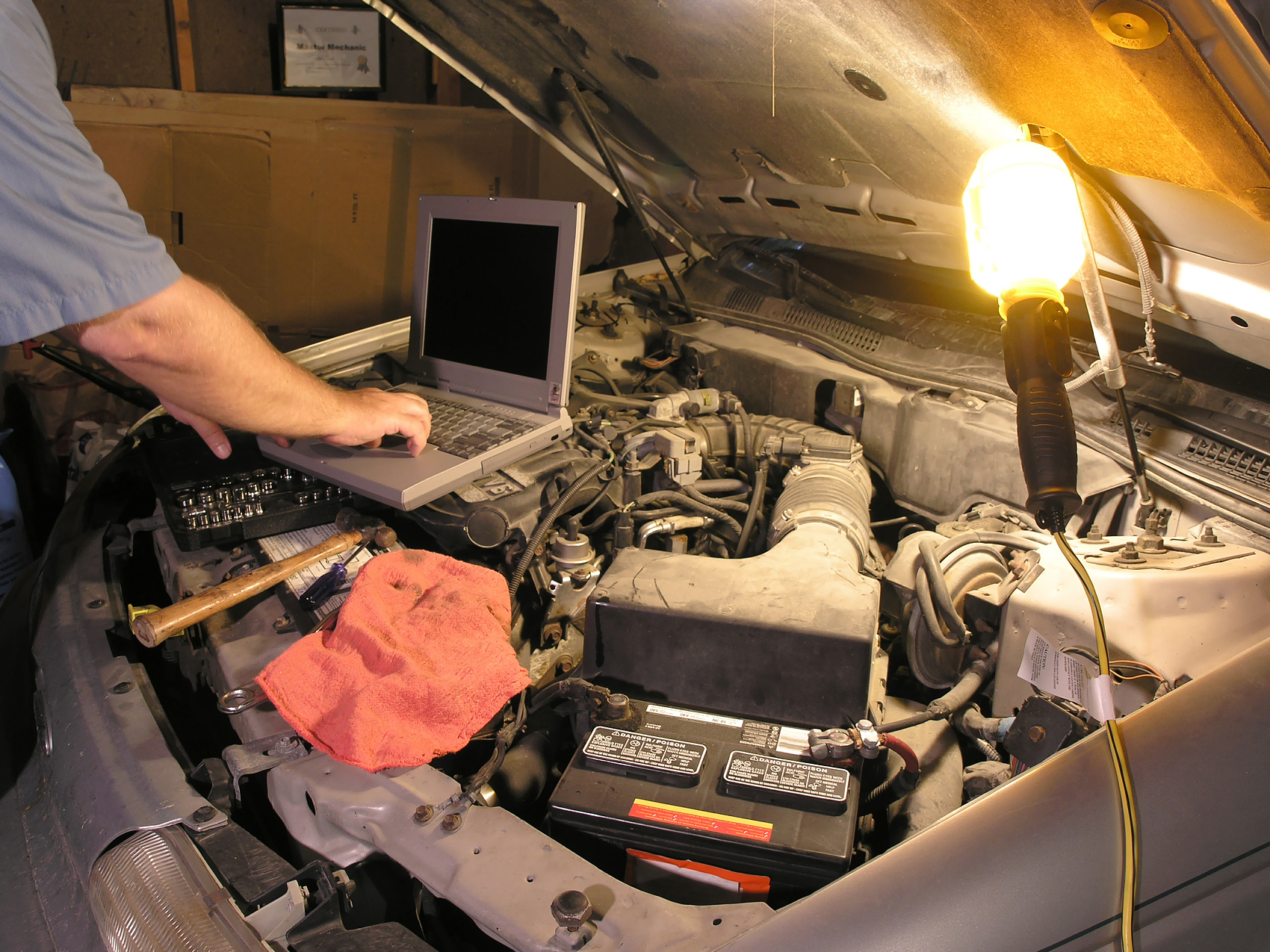
At its core, OBD2 works by connecting to a vehicle’s internal network through a port typically located under the dashboard. This port allows external devices, such as telematics units, to access the vehicle’s onboard computer. Once connected, the OBD2 system can retrieve a wealth of information, from engine RPM and coolant temperature to fault codes that indicate potential mechanical issues. This data is then transmitted to a fleet management system, where it is processed and analyzed to provide actionable insights.
Fleet management systems leverage OBD2 data to enhance vehicle tracking, maintenance scheduling, and driver behavior monitoring. For instance, by analyzing engine performance and fuel consumption patterns, fleet managers can identify inefficient driving habits and provide targeted training to drivers. This not only improves fuel efficiency but also reduces wear and tear on vehicles, extending their lifespan. Additionally, OBD2 data can alert fleet managers to potential mechanical issues before they become major problems, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
Another critical application of OBD2 in fleet management is compliance with environmental regulations. Many jurisdictions require fleets to monitor and report emissions data, and OBD2 systems provide the necessary information to ensure compliance. By integrating this data into a fleet management system, businesses can generate reports and maintain records effortlessly, avoiding costly fines and penalties.
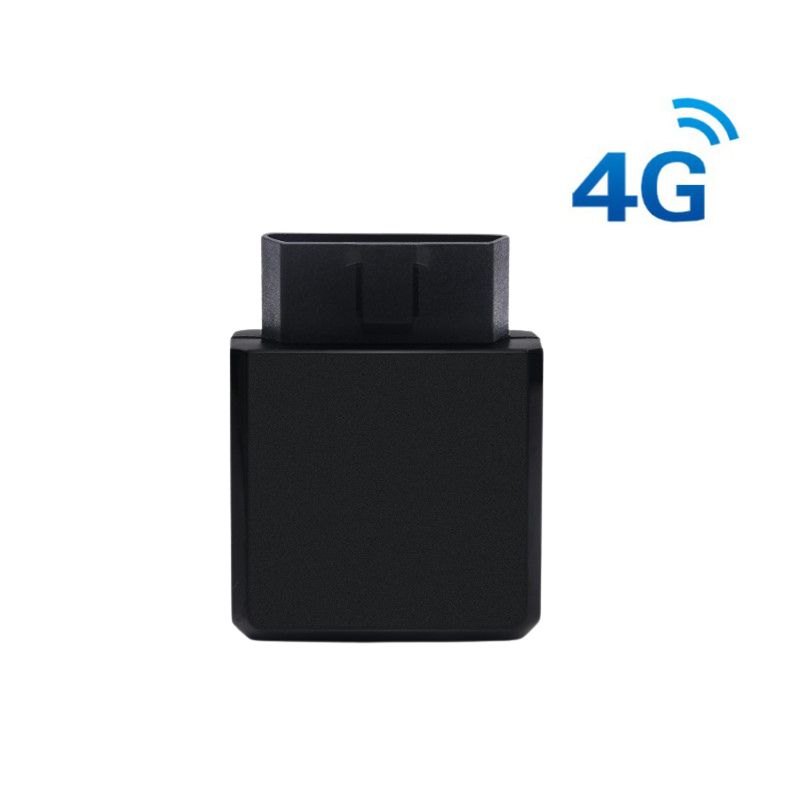

The synergy between OBD2 and fleet management systems also enhances safety. Real-time monitoring of vehicle diagnostics allows fleet managers to detect issues such as brake system malfunctions or tire pressure anomalies, which could pose safety risks. By addressing these issues promptly, fleets can reduce the likelihood of accidents and improve overall safety standards.
In conclusion, the combination of OBD2 technology and fleet management systems offers a powerful solution for modern fleet operations. By providing real-time insights into vehicle performance, maintenance needs, and driver behavior, this integration enables businesses to optimize efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure compliance. As technology continues to evolve, the role of OBD2 in fleet management will only grow, further transforming the way fleets are managed and maintained.