The car-sharing business model has emerged as a transformative force in the transportation industry, offering a flexible, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional car ownership. At its core, car sharing allows users to rent vehicles for short periods, often by the hour or minute, through a digital platform. This model has gained significant traction in urban areas, where the high cost of ownership, limited parking, and growing environmental concerns make shared mobility an attractive option. However, the success of car-sharing services hinges on efficient operations, seamless user experiences, and robust vehicle management systems. This is where OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) technology plays a pivotal role. By integrating OBD2 into car-sharing platforms, businesses can enhance functionality, optimize operations, and improve profit margins. This essay explores the car-sharing business model, its application functions, and the critical role of OBD2 in enabling its success.
Car sharing operates on a usage-based revenue model , where customers pay for the time or distance they use a vehicle. Unlike traditional car rental services, car sharing emphasizes convenience, with vehicles often available for pickup and drop-off at designated locations or through free-floating systems. The business model relies on several key components,Digital Platforms: Mobile apps or websites enable users to locate, book, and unlock vehicles,Fleet Management: Efficient management of vehicles, including maintenance, fueling, and redistribution,User Experience: Seamless access to vehicles, transparent pricing, and reliable service and Sustainability: Promoting eco-friendly transportation by reducing the number of privately owned vehicles.To remain competitive, car-sharing companies must minimize operational costs while maximizing vehicle utilization and customer satisfaction. This is where OBD2 technology becomes indispensable.
Car-sharing platforms rely on a suite of application functions to deliver a smooth user experience and ensure operational efficiency. These functions include:
Vehicle Location Tracking: GPS-enabled systems allow users to locate available vehicles in real time.Remote Access and Control: Users can unlock and start vehicles via mobile apps.Usage Monitoring: Tracking mileage, fuel levels, and battery status to optimize fleet management,Payment Integration: Automated billing based on usage time or distance, Maintenance Alerts: Notifications for scheduled maintenance or repairs, Driver Behavior Analysis: Monitoring driving patterns to ensure safety and reduce wear and tear.These functions are powered by data collected from vehicles, and OBD2 serves as the primary interface for accessing this data.

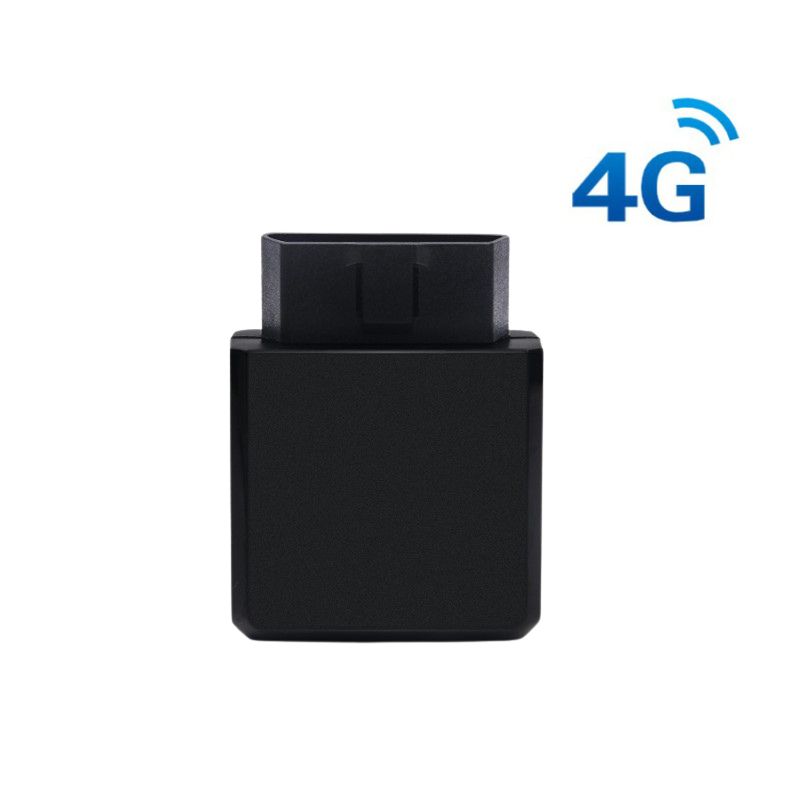
OBD2 is a standardized system that provides real-time data on a vehicle’s performance, emissions, and diagnostics. In the context of car sharing, OBD2 devices are installed in vehicles to enable a wide range of functionalities that enhance operational efficiency and user experience. Below are the key ways OBD2 contributes to the car-sharing business: It continuously collect data on engine performance, fuel consumption, mileage, and emissions. This data is transmitted to the car-sharing platform, enabling operators to monitor the health and status of each vehicle in real time. For example, if a vehicle’s fuel level is low, the system can alert the operator to schedule a refueling service. Similarly, if a vehicle reports a fault code, maintenance can be arranged promptly to minimize downtime. It enables remote diagnostics, allowing car-sharing companies to identify and address mechanical issues before they escalate. By analyzing fault codes and performance metrics, operators can schedule preventive maintenance, reducing the likelihood of breakdowns and extending the lifespan of their fleet. This proactive approach not only improves reliability but also lowers maintenance costs. Moreover , OBD2 data enhances the user experience by providing accurate information about vehicle availability, fuel levels, and battery status. For electric vehicles (EVs), OBD2 can monitor battery health and charging status, ensuring that users have access to vehicles with sufficient range. Additionally, OBD2 enables features like remote engine start and climate control, allowing users to pre-condition the vehicle before entering. Track ingdriving behavior, such as speed, acceleration, braking, and idling time. This data is invaluable for promoting safe driving practices and reducing wear and tear on vehicles. Car-sharing companies can use this information to incentivize good driving behavior, such as offering discounts to users who demonstrate safe driving habits, The wealth of data generated by OBD2 devices allows car-sharing companies to make informed decisions about fleet management, pricing, and service offerings. For example, analyzing usage patterns can help identify high-demand locations and times, enabling operators to optimize vehicle distribution and pricing strategies.
The integration of OBD2 technology directly impacts the profitability of car-sharing businesses by reducing operational costs and increasing revenue opportunities. Here’s how:
- Lower Maintenance Costs By enabling predictive maintenance, OBD2 helps car-sharing companies avoid costly repairs and minimize vehicle downtime. This not only reduces maintenance expenses but also ensures that more vehicles are available for use, increasing revenue potential.
- Improved Fleet Utilization Real-time monitoring and efficient maintenance scheduling ensure that vehicles are in optimal condition and available for use. This maximizes fleet utilization, a critical factor in achieving profitability in the car-sharing industry.
- Enhanced Customer Retention A seamless user experience, powered by OBD2 data, leads to higher customer satisfaction and retention. Satisfied customers are more likely to use the service repeatedly, driving recurring revenue.
- Reduced Fuel and Energy Costs ,OBD2 data on fuel efficiency and driving behavior can be used to optimize routes and promote eco-friendly driving habits. This reduces fuel consumption and energy costs, particularly for EVs.
- Data Monetization The data collected by OBD2 devices can be anonymized and sold to third parties, such as insurance companies or urban planners, creating an additional revenue stream.
While OBD2 offers significant benefits, its implementation in car sharing is not without challenges. These include the cost of OBD2 devices, data security concerns, and the need for robust connectivity infrastructure. However, advancements in IoT (Internet of Things) and 5G technology are addressing these challenges, making OBD2 more accessible and reliable.
Looking ahead, the role of OBD2 in car sharing is expected to grow as the industry evolves. The rise of autonomous vehicles and smart cities will further enhance the capabilities of OBD2, enabling even greater efficiency and innovation in shared mobility.
Comprehensively,The car-sharing business model represents a paradigm shift in urban transportation, offering a sustainable and convenient alternative to traditional car ownership. OBD2 technology plays a critical role in enabling this model by providing real-time data, enhancing operational efficiency, and improving user experiences. By leveraging OBD2, car-sharing companies can reduce costs, increase revenue, and achieve higher profit margins. As the industry continues to evolve, OBD2 will remain a cornerstone of innovation, driving the future of shared mobility.